Today most of us are consuming an excess amount of salt than the requirement. The average per-person salt intake is too high, between 9 to 12 grams per day. Habitual intake of excess salt is the main culprit behind the widespread prevalence of hypertension (high blood pressure). To prevent and treat hypertension and other cardiac problems, taking a low-sodium diet is essential. Reducing the daily salt intake to not more than 6g (approximately of 1 teaspoon of salt per day) is effective to reduce blood pressure. (1)
Low Sodium Indian Diet – How to make it happen?
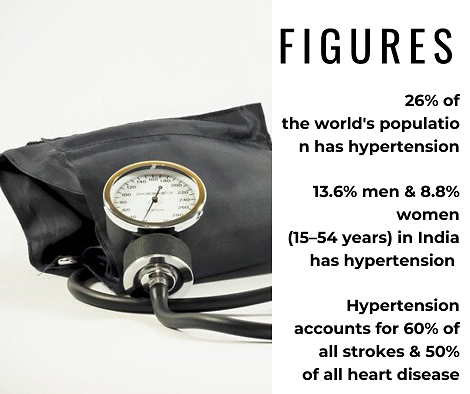
Hypertension-salt-sodium :The relation
Scientific studies confirm that a modest reduction in salt intake lowers blood pressure in people with hypertension in all age groups, and ethnic groups. Reduction in blood pressure reduces the risk of reducing strokes, heart attacks, and heart failure. (1,4,5) Therefore Reduction in salt intake is one of the most cost-effective interventions to minimize the incidence of heart disease and stroke.
Daily intake of an excessive amount of common salt (sodium chloride) introduces an excess amount of sodium in the body, which holds extra water, disrupting the fluid balance and thus increasing the blood volume and blood pressure. Elimination of excess salt by kidneys creates extra strain on the renal system which increases the risk of renal problems. Consistent high blood pressure is bad for brain health and increases the risk of dementia. (1,2,4)
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommended that an adult should consume less than 2000mg of sodium (sodium), or 5g of common salt daily. (3)
Basic functions of Sodium
- Sodium is an essential nutrient necessary for the maintenance of plasma volume.
- It regulates the acid-base balance of the body.
- It is needed for the transmission of nerve impulses.
- It is essential for normal cell functions.
- It maintains our blood pressure.
- It regulates the distribution of water in different body compartments.
What are the sources of sodium in the diet?
Food processing reduces the potassium content of the food. A diet high in processed foods and low in fresh fruits and vegetables are often lacking in potassium and high in sodium. This puts the person at risk for raised blood pressure and related non-communicable diseases. (4)
Table salt is pure sodium chloride, the prime source of sodium.
- All types of edible salts like rock salt, black salt, pink Himalayan salt, low sodium salt is sodium chloride salt along with the little amount of other salts.
- Sodium is naturally present in most animal foods such as milk, meat, and shellfish.
- Many condiments like soy and fish sauces are rich sources of sodium.
- Processed foods such as bread, crackers, meats contain a high amount of salt.
- Snack foods and fast foods usually contain high amounts of sodium. (4)
We should consume the above-mentioned sodium-rich foods in moderation.

Tips for preparing a low sodium diet
The majority of sodium in our diets comes from packaged and restaurant food and is a direct result of food processing. Even foods that may not taste salty can be major sources of sodium. Foods with only moderate amounts of sodium, such as bread, can be major sources in our diets because we eat so much of them. You can reduce your daily sodium intake by following a few simple tips. (6,7,8,9) We can categorize the tips into 3 sets –
- Shopping tips
- Cooking tips
- Eating tips
Shopping tips: Tips to follow while planning for regular grocery shopping
1. Buy more fresh seasonal vegetables & fruits and avoid their preserved counterparts like canned, frozen vegetables as much as possible
2. Limit purchasing sauces (pasta sauce, tomato sauce, soy sauce, chili sauce, etc)-, mixes, and “instant” products, including flavored rice, instant noodles, and ready-made pasta.
3. Reduce the frequency of buying processed breakfast cereals, rather than encourage family members for homemade breakfast like roti, puri, Dalia, poha, etc.
4. Prefer buying the packaged foods labeled as “low sodium,” “reduced sodium,” or “no salt added” if available.
5. Purchase freshly slaughtered animal foods like mutton, chicken, pork, beef, etc., and reduce the intake of cured, salted, smoked, and other processed meats.
6. Avoid salted nuts, buy simple unsalted nuts instead.
7. Limit spending on vegetable pickles. These are high-sodium foods.

Cooking tips: Tips to remember while cooking regular food
8. Reduce the use of salt in cooking. Remember human taste buds cannot detect a minor reduction in the salt of about 30%. So, reduce the amount of salt in your recipes gradually.
9. Mix table salt and black salt to reduce the sodium content. Commonly used table salt is pure sodium chloride (NaCl) whereas black salt is a natural salt, containing principally sodium chloride along with traces of other salts.1 g of common salt (sodium chloride) contains 390 mg sodium whereas 1 g of black salt contains 378.3 mg of sodium. You can mix 500 grams of common salt with 500 grams of black salt, mix well and use this for cooking purposes. This salt mixture is healthier than pure sodium chloride (table salt or common salt).
10. Don’t use salt in making chapati or roti.
11. Don’t add salt in freshly cut fruits like cucumber or banana. Enjoy the unique, original taste of the particular food.
12. Reduce the use of salt in making salad and soup.
13. Use salt substitutes, garlic, citrus juice, salt-free seasonings, or spices in the cooking.
Eating tips: Tips to follow in the daily diet
14. Avoid taking any extra salt to foods while eating.
15. Consume more milk, yogurt, and panner and reduce taking salted buttermilk, cheese as far as possible as both cheese and buttermilk are rich sources of sodium chloride.
16. Limit the intake of bread and biscuits which are rich sources of sodium.
17. Reduce eating outside food as restaurant foods usually contain more salt than homemade foods.
18. Reduce the intake of fast foods that are rich in sodium but poor in other nutrients.
19. Eat smaller portions of salty foods. There is no need to eliminate your favorite high-sodium recipes like soy sauce, salted pickles, and fish, or cheese but reduce the frequency and quantity.
20. Consume more fresh fish, and avoid salted and dried fish, commonly called “sutkimach”.
21. Moreover, Habituate your child with low salt from early childhood. The tendency of high blood pressure starts to develop from childhood due to excess salt intake and an unhealthy lifestyle. Don’t let their taste buds get adjusted with high salt.

Bottom Line
Hypertension is like an epidemic now. Sodium plays a huge role in controlling blood pressure. Sodium is an essential mineral required for our normal body functions. All types of salts like table salt, black salt, rock salt, pink Himalayan salts, etc contain principally sodium chloride (NaCl). So reducing salt intake is essential for keeping blood pressure under check. All-natural foods contain traces of sodium along with other minerals. But the processing of foods increases the sodium content of foods as a substantial amount of sodium is added to the foods during processing. Therefore, it is always better to choose freshly available fruits and vegetables rather than their processed counterparts. Be mindful while eating. Follow the simple tips mentioned above to reduce sodium intake from your daily diet.





